The growing adoption of renewable energy sources has placed solar power at the forefront of the shift towards sustainable energy solutions. Solar panels, which convert sunlight into electrical energy, are central to this transformation.
Understanding the various components of solar panels and their respective functions is essential for grasping how these systems operate. This article delves into the common parts of solar panels and their specific roles in generating clean energy.
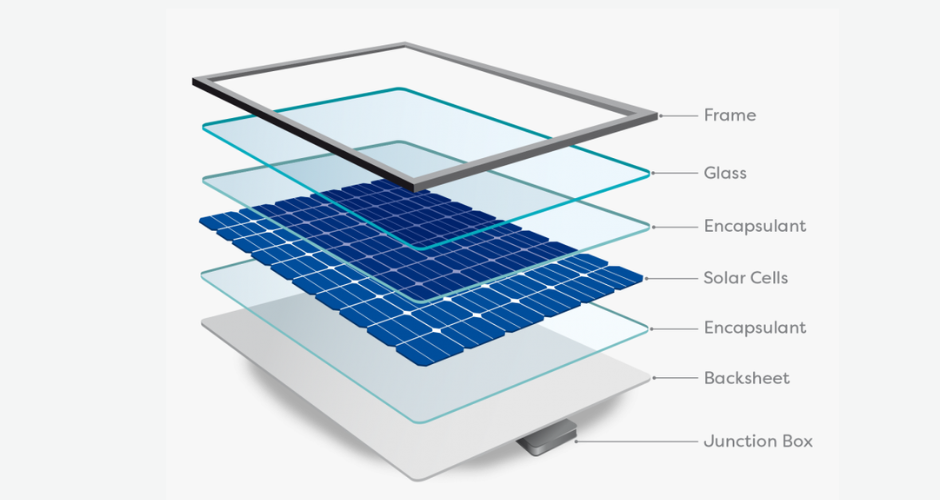
Photovoltaic cells form the core of solar panels and are responsible for converting sunlight into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the PV cells, it energizes electrons in the semiconductor material, typically silicon. This excitement generates an electric current.
Monocrystalline Silicon Cells: Known for their high efficiency and longevity, these cells are made from a single continuous crystal structure.
Polycrystalline Silicon Cells: These cells are made from multiple silicon crystals melted together, generally offering a lower efficiency than monocrystalline cells but at a reduced cost.
Thin-Film Solar Cells: Made from materials like cadmium telluride or amorphous silicon, these cells are lightweight and flexible but usually less efficient than their crystalline counterparts.
The glass cover protects the PV cells from environmental factors such as rain, dust, and physical damage. It also plays a critical role in allowing maximum sunlight to reach the cells while minimising reflection and enhancing durability.
Transparency: High-quality glass ensures maximum light penetration.
Durability: It must withstand various weather conditions, including hail, wind, and extreme temperatures.
Anti-Reflective Coating: Often included to reduce reflection and improve light absorption by the cells.
The encapsulant is a layer of material that surrounds the PV cells, providing protection and maintaining their performance over time. It acts as a shock absorber and protects the cells from moisture and contamination.
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA): The most common encapsulant material, known for its excellent transparency and adhesive properties.
Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB): Used in some panels for its enhanced mechanical strength and durability.
The back sheet is the outermost layer at the rear of the solar panel, providing electrical insulation and protection from environmental damage. It helps prevent moisture infiltration while also providing structural support.
Polyvinyl Fluoride (PVF): Known for its excellent weather resistance.
Polyester Films: Often used for their durability and cost-effectiveness.
The frame provides structural integrity to the solar panel, ensuring it can be mounted securely and withstand environmental stresses. It also assists in the safe handling and installation of the panels.
Aluminum: The most common material, chosen for its lightweight, strength, and resistance to corrosion.
Steel: Sometimes used for increased strength, though it is heavier than aluminum.
Important note: Potentia Engineering specialises in a diverse range of solar solutions for both residential and commercial properties throughout the United Kingdom. Our services encompass Solar PV Panels, EV Charging Infrastructure, and cutting-edge Batteries & storage solutions.
Committed to sustainability and pioneering innovation, we deliver bespoke solar installations designed to optimise energy efficiency and reduce costs. With a track record of managing some of the UK's most expensive commercial solar projects for esteemed clients like Jaguar and Land Rover, we bring unparalleled expertise to every endeavour. We will also help you to install solar with zero capital. Trust Potentia Engineering for reliable, eco-friendly energy solutions.

The junction box, located on the back of the solar panel, houses the electrical connections and serves as a point for external wiring to connect to the panel. It often includes bypass diodes to manage shading issues and protect the PV cells.
Bypass Diodes: Prevent power loss due to shading by allowing current to bypass shaded cells.
Terminal Connections: Enable the connection between the panel and the external electrical system.
Wiring and connectors facilitate the flow of electricity generated by the PV cells to the external electrical system. They are designed to handle the electrical output of the panels and ensure secure, weather-resistant connections.
MC4 Connectors: Commonly used for their ease of installation and reliability.
PV Wire: A specialised wire designed to withstand high temperatures and UV exposure.
The mounting system secures solar panels to roofs, ground mounts, or other structures. It must be robust enough to endure various environmental conditions and ensure the optimal angle for maximum sunlight exposure.
Roof Mounts: Attached directly to the roof of a building, available in different designs to suit various roof types.
Ground Mounts: Installed on the ground, often used in large-scale solar farms.
Pole Mounts: Panels are mounted on poles, which can be manually or automatically adjusted to track the sun.
Related Article:
DIY Vs Hiring a Solar Panel Installation Company – Guide 2024
What is Solar PPA? – Components and Benefits
How Commercial Businesses Can Benefit from Solar System Investments?
While not a physical part of the panel itself, the inverter is crucial in a solar power system. It converts the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) used by most household appliances and the grid.
String Inverters: Connect multiple solar panels in series, converting their combined DC output into AC.
Microinverters: Attached to individual solar panels, converting DC to AC at the panel level, offering better performance in shaded conditions.
Hybrid Inverters: Combine solar and battery inverters into one unit, managing energy from both solar panels and batteries.
Battery storage systems store excess electricity generated by solar panels for use during periods when the panels are not producing electricity, such as at night or during cloudy weather. This ensures a continuous power supply and enhances energy independence.
Lead-Acid Batteries: Cost-effective but with a shorter lifespan and lower efficiency.
Lithium-Ion Batteries: Offer greater efficiency, a longer lifespan, and higher energy density, though they are more expensive.
Solar panels are complex systems made up of various components, each playing a vital role in converting sunlight into usable electricity.
As technology advances, these components continue to evolve, enhancing the efficiency, durability, and affordability of solar power systems, and driving the world closer to a sustainable energy future.

We pride ourselves on giving an exceptional level of customer service. Contact us to day for a no obligation quote.



If you would like to receive a personalised quote for any or our services, or just have general queries about Solar energy systems please complete the form below. We aim to get back to you within 24 hours.